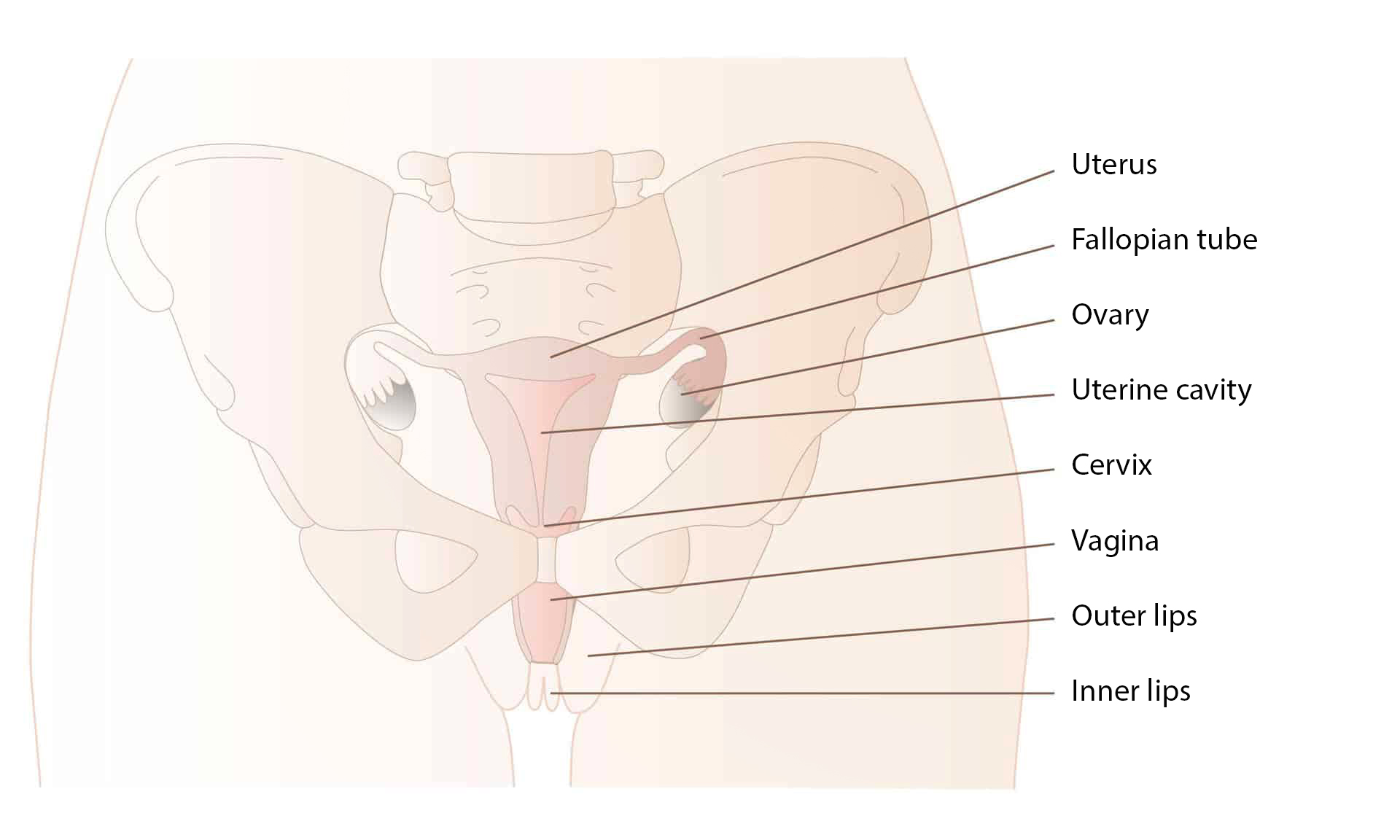
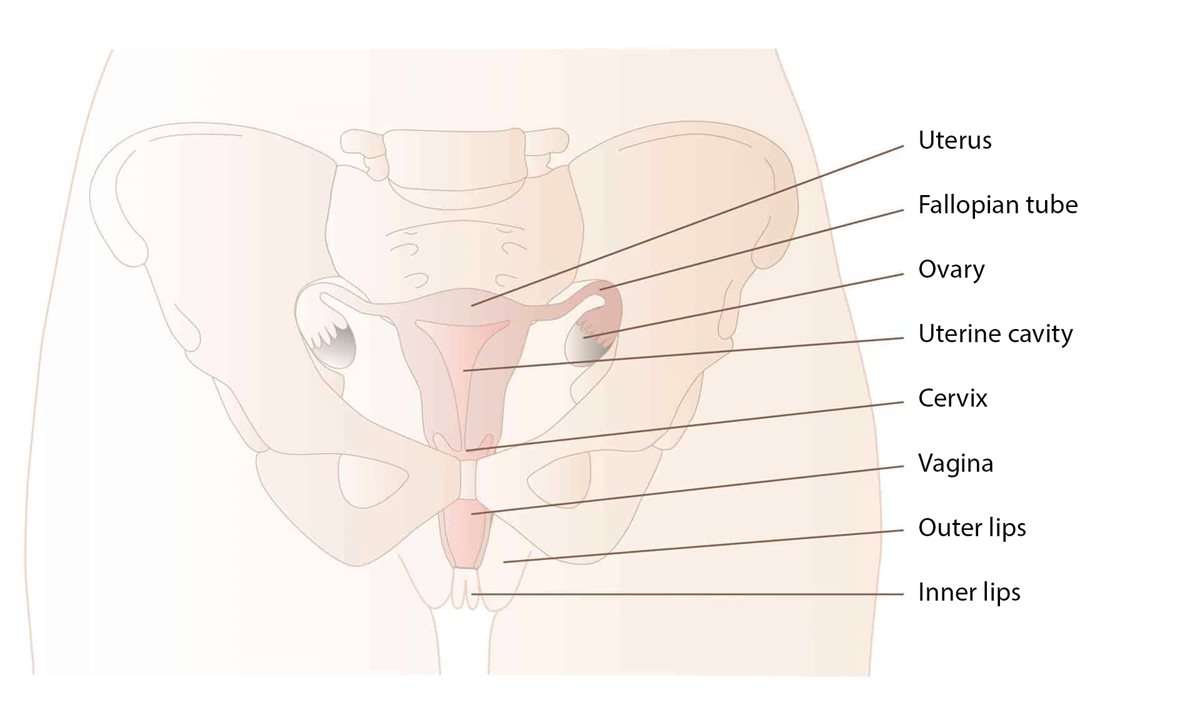
Womb
The womb (or uterus) is part of a woman’s internal genitalia and consists of a muscle the size and shape of a pear. The womb is situated between the bladder and the rectum. In the top of the womb a Fallopian tube leads to each side, these end in the ovaries and collect the egg cells that the ovaries produce. The womb ends in the cervix which lies uppermost most in the vagina.
When an egg cell has joined with a sperm cell it attaches itself to the inside of the womb and starts to grow. A placenta also develops, through which the baby will be nourished. After about 40 weeks the baby is big enough to be born. At this point the muscle in the womb constricts so that the baby can be born through the vagina. The womb can be the size of a football just after birth, but it soon returns to the size of a pear.
We are in the process of translating the full content of this website to English.
Translated material will be published consecutively as soon as it is ready.
There are about 1300 questions with answers, as well as many articles that need to be translated.
We ask for your patience and understanding for this.